Answer:
Option B
Explanation:
Plan alkenes declourise Br2 water
cis-isomer $\underrightarrow{ dil.KMnO_{4}}$ Meso isomers by syn addition
trans-isomer $\underrightarrow{ dil.KMnO_{4}}$ d(+) and l(-) isomers by syn addition
thus, reacemic mixture
Formation of anhydride from dicarboxylic acid indicates cis-isomer
P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acids
P,Q $\underrightarrow{ Br_{2} water}$ decolourised
P and Q have (C=C) bond
P $\underrightarrow{\triangle}$ anhydride
Thus , P is cis-isomer
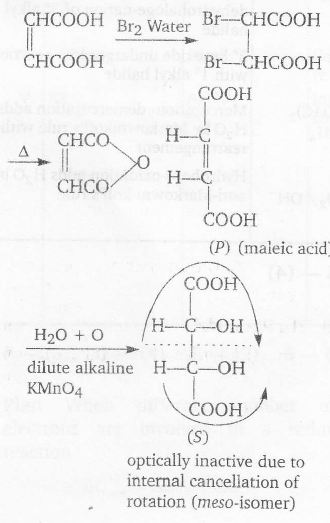
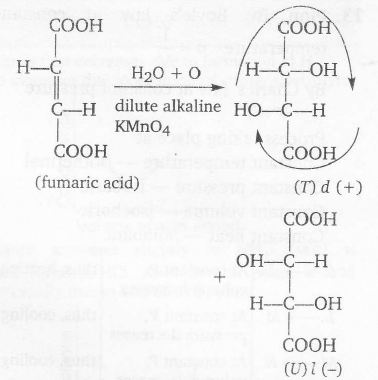
T and U (in 1:1 molar ratio) form optically inactive (racemic mixture) due to external cancellation