Answer:
Option D
Explanation:
Using geometry
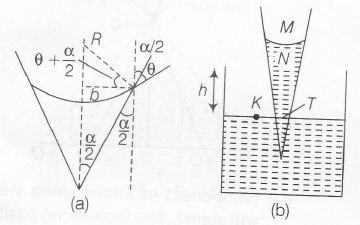
$\frac{b}{R}=\cos(\theta+\frac{\alpha}{2})$
$\Rightarrow $ $ R=\frac{b}{\cos(\theta+\frac{\alpha}{2})}$
Using pressure equation along the path MNTK
$p_{0}-\frac{2S}{R}+h\rho g=p_{0}$
Substituting the value of R , we get
$h=\frac{2S}{R\rho g}$
$=\frac{2S}{b\rho g}\cos(\theta+\frac{\alpha}{2})$