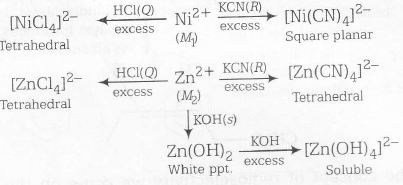Answer:
Option B
Explanation:
Plan This problem can be solved by using the concept of chemical reaction of transition metal ions (.) colour and structure of transition metal compounds.
Here, among given four option Ni2+ and Zn2+ has ability to form tetrahedral as well as square planar complex depending upon types of reagent used.
Ni2+ on reaction with KCN forms square planar complex [Ni(CN)4]2- due to strong field strength of CN.
Ni2+ + KCN $\rightarrow$ [Ni(CN)4]2- (Square Planar)
while on reaction with HCl.Ni2+ forms a stable tetrahedral complex [Ni(Cl)4]2-.
Zn2+, on the other hand on reaction with KCN as well as HCl, produces tetrahedral complex because of its d10 electronic configuration.
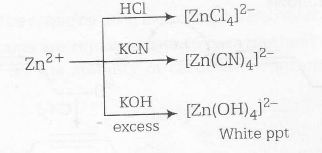
Complete reaction sequence can be shown as