Answer:
Option C
Explanation:
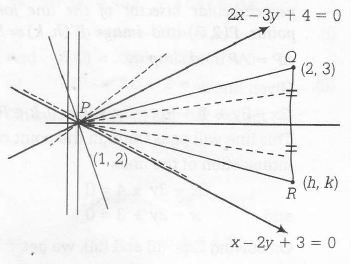
Central Idea First of all find the point of intersection of the lines 2x-3y+4=0 and x-2y+3=0 (say A) . Now , the line
(2x-3y+4) +k(x-2y+3)=0 is the perpendicular bisector of the line joining points P(2,3) and image P ' (h,k). Now AP= AP ' and simplify
Given line is
(2x-3y+4)+k(x-2y+3)=0 , k ε R ..... (i)
This line will pass through the point of intersection of the lines
2x-3y+4= 0 .......(ii)
and x-2y+3= 0 ..........(iii)
On solving Eqs (ii) and (iii), we get
x=1, y=2
$\therefore$ Point of intersection of lines (ii) and (iii) is (1,2)
Let M be the mid-point of PP' , then AM is perpendicular bisector of PP' (where A, is the point of intersection of given lines )
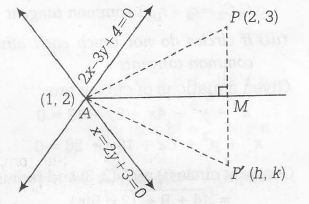
$\therefore$ AP=AP'
$\Rightarrow$ $\sqrt{(2-1)^{2}+(3-2)^{2}}=\sqrt{(h-1)^{2}+(k-2)^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\sqrt{2}=\sqrt{h^{2}+k^{2}-2h-4k+1+4}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\sqrt{2}=\sqrt{h^{2}+k^{2}-2h-4k+5}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\sqrt{2}=\sqrt{h^{2}+k^{2}-2h-4k+5}$
$\Rightarrow$ $h^{2}+k^{2}-2h-4k+3=0$
Thus , the required locus is
$x^{2}+y^{2}-2x-4y+3=0$
which is a equation of circle with
radius = $\sqrt{1+4-3}=\sqrt{2}$
Aliter
(2x-3y+4)+k(x-2y+3)=0 is family of line passing through (1,2) By congruency of triangles . We can prove that mirror image (h,k) and the point (2,3) will be equidistant from (1,2)
$\therefore$ Locus of (h,k) PR=PQ
$\Rightarrow (h-1)^{2}+(k-2)^{2}= (2-1)^{2}+(3-2)^{2}$
or $ (x-1)^{2}+(y-2)^{2}= 2$
$\therefore$ Locus is a circle of radius = $\sqrt{2}$