Answer:
Option (A,B,C,D)
Explanation:
Due to symmetry on upper side and lower side, points P and Q are at same potentials. Similarly, points S and T are at same potentials. Therefore, the simple circuit can be drawn as shown
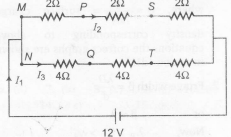
$I_{2}= \frac{12}{2+2+2}=2A$
$I_{3}=\frac{12}{4+4+4}=1A$
$\therefore$ $I_{1}=I_{2}+I_{3}=3A$
$I_{PQ}=0$ because $V_{p}=V_{Q}$ Potential drop (from left to right) across each resistance is
$\frac{12}{3}=4V$
$\therefore$ $V_{MS}=2 \times 4=8V$
$V_{NQ}=1 \times 4=4V$
or $V_{S} < V_{Q}$